“`html
Robotic Structural Profiler Installed
GIS Enhances Capabilities with High-Tech Plasma Cutter
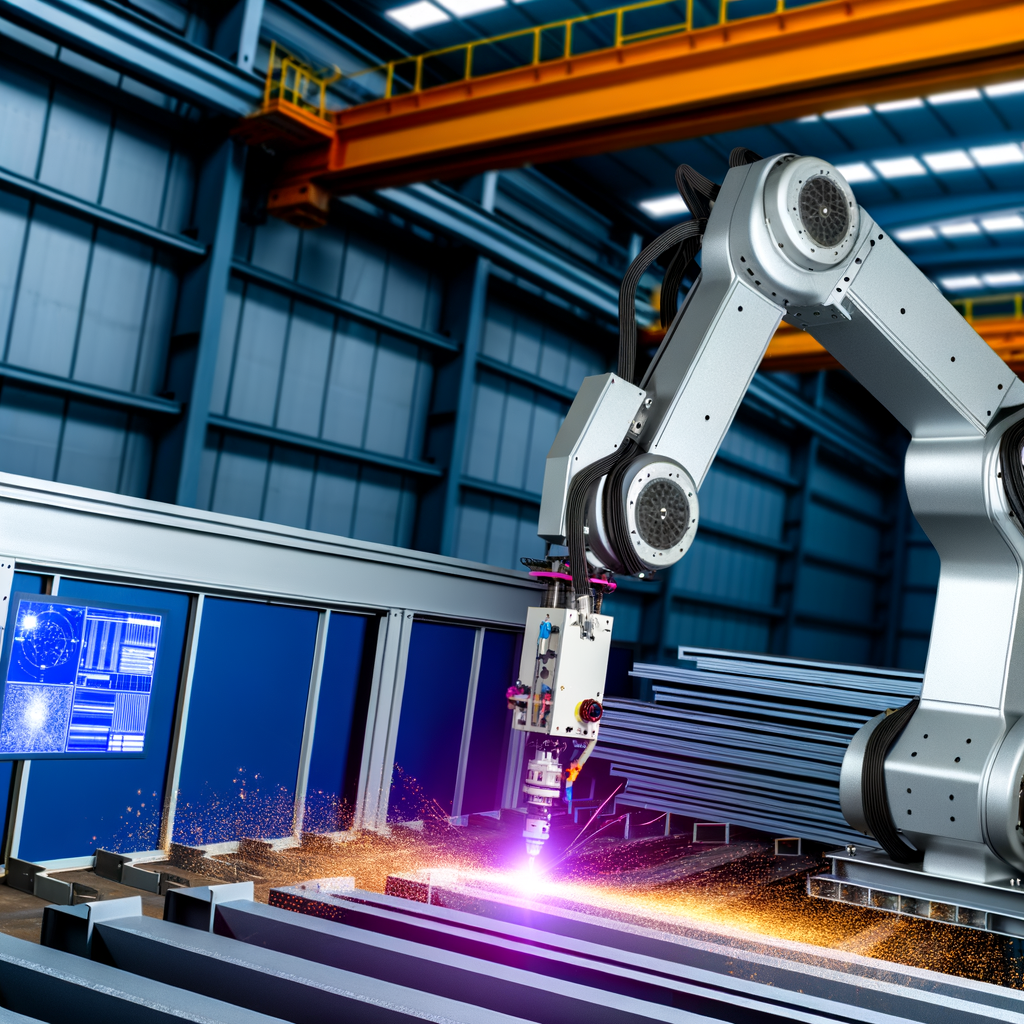
In a major leap toward streamlined structural profiling, GIS has installed a robotic structural profiler that’s ready to revolutionize the way heavy materials are cut. The latest technological addition to their already enviable array of machinery, this high-tech robotic profiler is designed to offer precision, speed, and versatility – the three holy grails of industrial material handling.
Fusing Modern Robotics and Plasma Cutting
Now let’s talk tech. The new profiler combines robotic technology with plasma cutting capabilities, making it a versatile and highly efficient system for profiling structural steel. The advantage of plasma cutting, of course, lies in its ability to cut thick materials with exceptional precision, while the incorporation of robotic systems ensures that the cuts are automatically programmed.
With this installation, GIS is not just sharpening its literal tools but is also upping the ante in the broader competitiveness of the industry. Introducing robotics promises fewer operational errors, increased throughput, and a more cost-effective process – aspects that any fabricator worth their salt would be thrilled to achieve.
Why This Matters For Structural Profiling
Plasma profiling may sound like a niche practice, but for industries working with large and heavy materials, it’s critical. Steel beams and other raw materials often need precise cuts to fit seamlessly into construction, machinery, or other applications. Here’s why innovations like GIS’s robotic structural profiler are game-changers:
- Precision: Robotic systems can handle complex and intricate cuts with better accuracy than manual labor or older automated systems. Think of the most complicated steel beams and components — One wrong cut could compromise an entire structure.
- Consistency: Human fatigue and errors? Forget about it. Robotics ensures that every cut, no matter the length of operation, remains consistent throughout.
- Efficiency: Time is money, especially in an industry that deals with massive projects. Robotics eliminates much of the inefficiency that naturally occurs in traditional systems. GIS can now handle more projects in less time, all with the same or even improved quality.
- Customization: The use of robotic tech allows for extensive customization, with automated software capable of adjusting for different materials, cutting angles, lengths, and other specifications. Ultimately, this means fewer bottlenecks and shedding time off on-site adjustments.
Going Green(er)
Notably, adding robotic precision also helps minimize waste. By allowing for more exact cuts, GIS is helping to reduce the amount of extra material—whether it’s metals or consumables like grinding wheels or torches—that needs to be thrown away. More precision = less waste, and less waste = less environmental impact. This kind of responsible manufacturing is part of the broader push within the industry to embrace sustainability, an oft-overlooked but critical measure in metal fabrication.
The Significance for GIS and Its Clients
GIS’s investment is in itself a bold statement about its commitment to advancing its capabilities. Whether it’s in meeting the highly volatile demands of the aerospace industry, helping with large-scale infrastructure projects, or refining machinery manufacturing, clients can now benefit from enhanced services where time savings, quality control, and reduced costs become the new norm.
For their clients, that means projects completed faster and with higher-quality outcomes. It’s like upgrading from driving an old manual car to a cutting-edge, self-driving electric vehicle. The premise is the same—get from A to B—but the process is far smoother and more efficient.
Final Thoughts
While it may seem like an incremental improvement on the surface, GIS’s new robotic structural profiler is a gateway to faster production, higher accuracy, and significantly reduced waste. In a world where timelines are tight, and competition is fierce, this installation will certainly position GIS as a key player, not just abreast of the industry standard but ahead of it. Robotics, plasma cutting, and sustainability are no longer luxury options—they’re pillars of a rapidly evolving industrial age.
As GIS sharpens its focus on technology, it’s hard not to be excited about the present—and future—applications of its cutting-edge robotic capabilities. After all, the future of fabrication is here, and it’s sharply profiled!
“`